Top 10 Tribal Superfoods: A Journey into Indigenous Nutrition
Tribal communities across the world have relied on nature for sustenance, creating diets rich in nutrients and health benefits. These superfoods, derived from ancient practices, offer a glimpse into their connection with the environment. Here are the top 10 tribal superfoods celebrated for their nutritional and medicinal properties:
- Millets (Ragi, Bajra, and Jowar)
A staple in many tribal diets, millets are gluten-free, rich in fiber, and packed with essential nutrients like iron, calcium, and protein. Tribes in India, Africa, and South America have relied on these grains for centuries to maintain energy and improve digestive health.
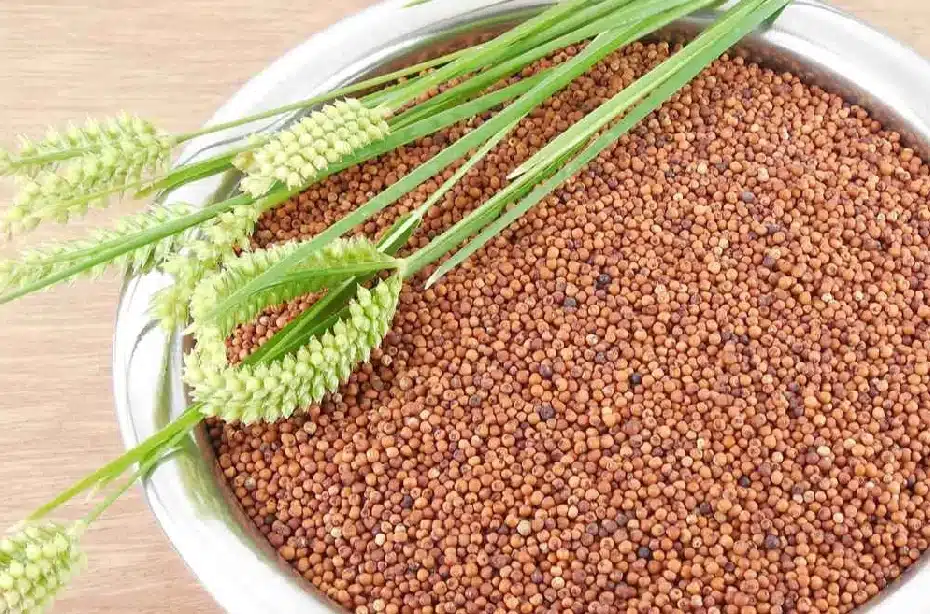

Ragi
Health Benefits:
Promotes bone health
Manages diabetes
Boosts heart health
- Wild Honey
Collected from forest bees, wild honey is an integral part of many tribal diets. Known for its antioxidant properties, it serves as a natural sweetener and a remedy for various ailments.

Health Benefits:
Strengthens immunity
Treats cough and throat infections
Enhances skin health
- Bael Fruit
The bael tree (Aegle marmelos) is sacred to many Indian tribes. Its fruit is loaded with vitamins A, B, and C, along with antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties.
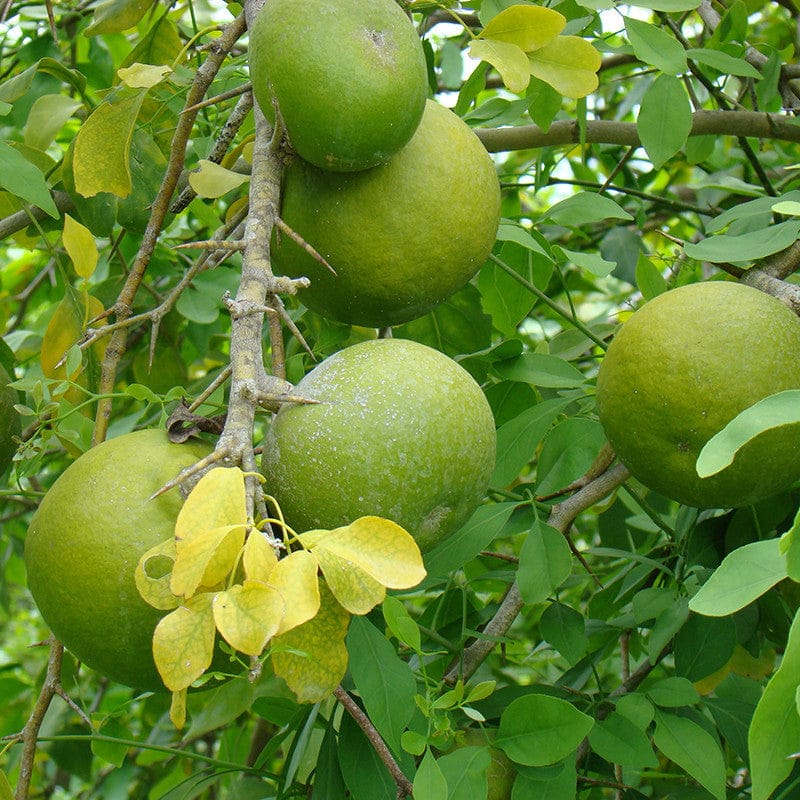

Health Benefits:
Aids digestion
Helps in managing diabetes
Detoxifies the liver
- Moringa (Drumstick Tree)
Tribes across Africa and Asia call moringa a “miracle tree.” Every part of it—leaves, pods, and seeds—is rich in nutrients like iron, calcium, and amino acids.

Health Benefits:
Boosts energy levels
Supports brain health
Promotes wound healing
- Mahua Flowers
Collected by tribal communities in central India, mahua flowers are rich in natural sugars, vitamins, and minerals. Traditionally, they are used to make beverages, sweets, and medicines.
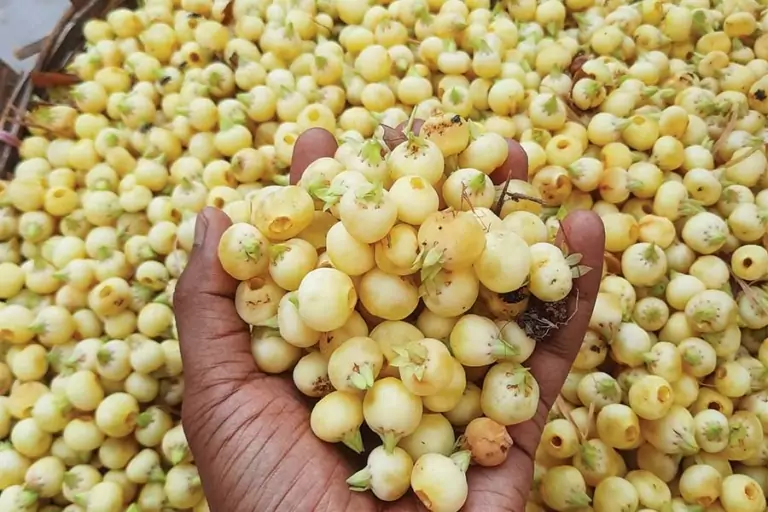

Health Benefits:
Improves energy levels
Enhances reproductive health
Fights malnutrition
- Turmeric
A sacred spice in many tribal cultures, turmeric contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compound. Tribal remedies often include turmeric for treating wounds and infections.

Health Benefits:
Reduces inflammation
Boosts immunity
Improves skin health
- Wild Berries (Jamun, Gooseberry, Ber)
Tribes often consume wild berries for their rich vitamin C content and antioxidant properties. These fruits play a key role in maintaining gut and heart health.
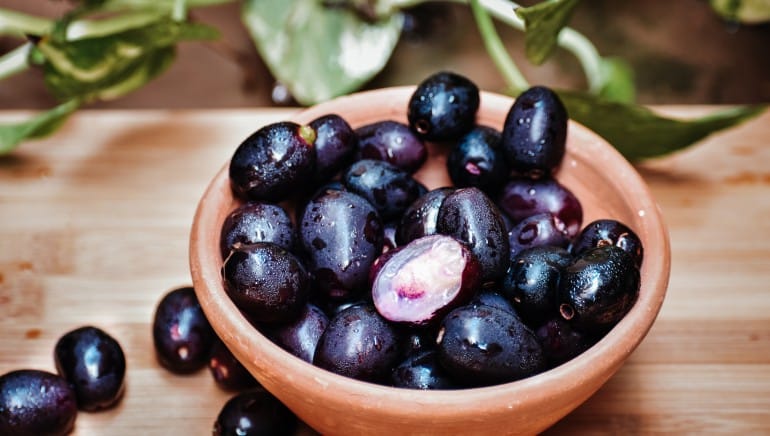

Health Benefits:
Regulates blood sugar levels
Enhances digestion
Improves eye health
- Amaranth Leaves and Seeds
Amaranth is a pseudo-cereal revered by tribal communities for its high protein, iron, and calcium content. Both the leaves and seeds are highly nutritious.
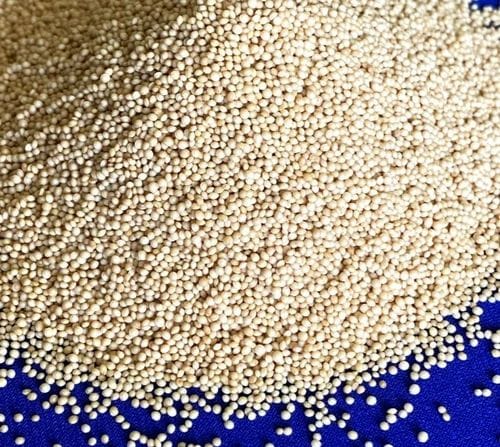

Health Benefits:
Strengthens bones
Supports muscle growth
Improves cardiovascular health
- Bamboo Shoots
Common among Asian and Northeast Indian tribes, bamboo shoots are rich in dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals like potassium and manganese.
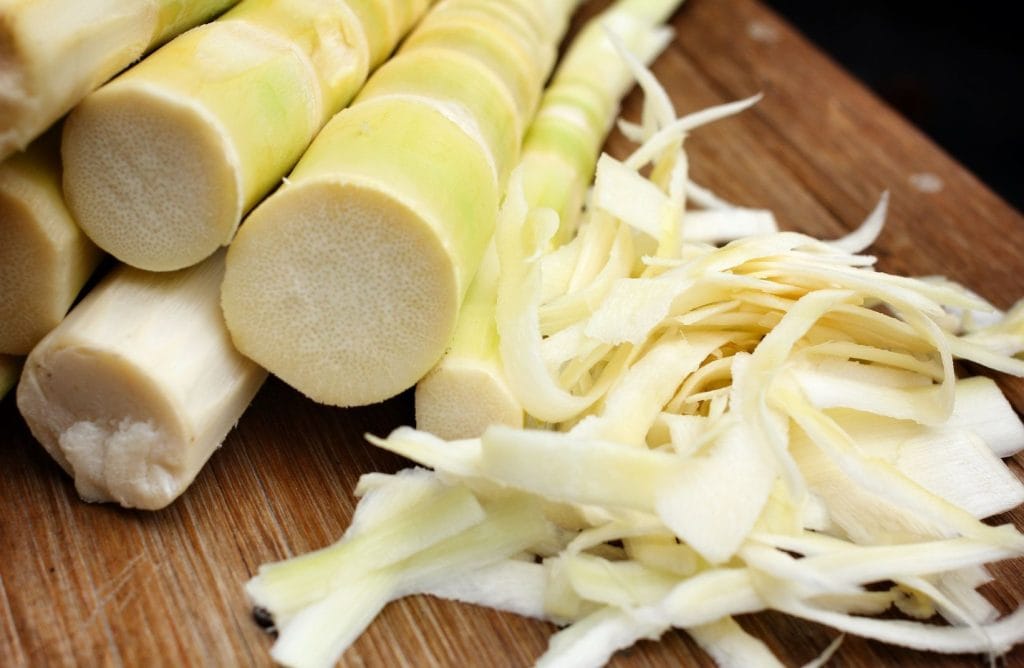

Health Benefits:
Lowers cholesterol
Promotes digestive health
Boosts immune function
- Jackfruit Seeds
A common food in tropical regions, jackfruit seeds are often boiled or roasted by tribal communities. They are rich in protein, vitamins, and antioxidants.
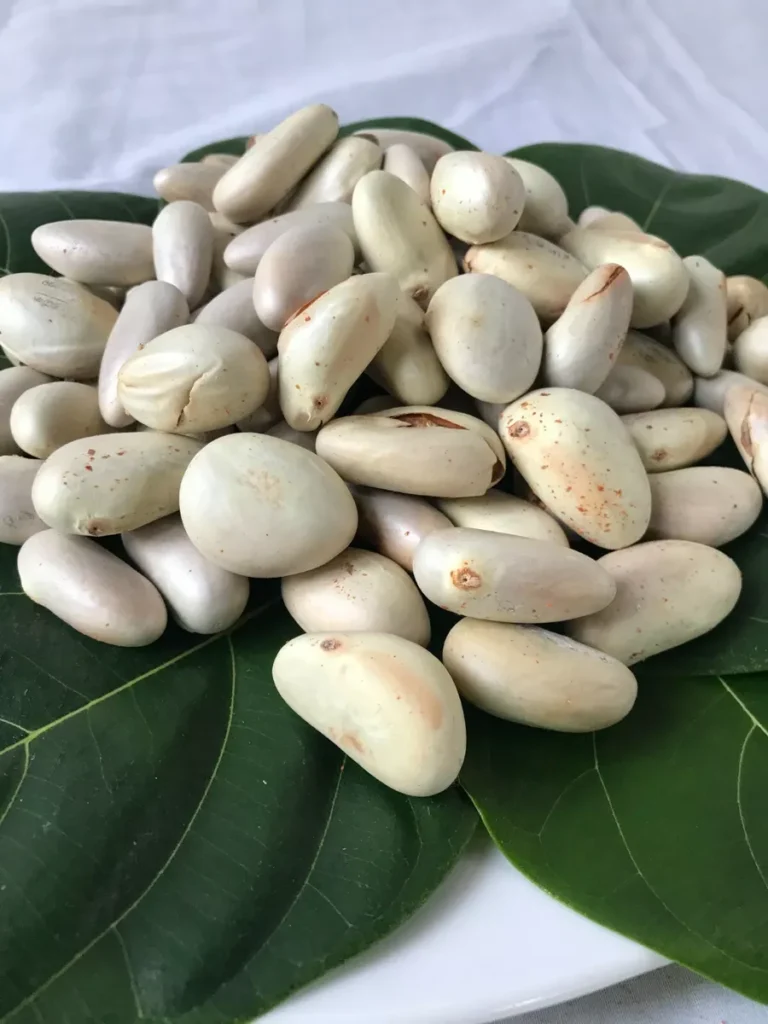

Health Benefits:
Improves energy levels
Aids digestion
Supports weight management
These tribal superfoods are not just nutrition-packed; they reflect centuries of indigenous knowledge and sustainable practices. Integrating them into modern diets can promote health, connect us with nature, and preserve tribal heritage.